A European research team investigated the impact of sand and dust pollution on Oman's photovoltaic modules. They collected 60 samples from different seasons, months, and tilt angles.
The study points out that "the loss of sand and dust pollution largely depends on the particle size, shape, and related spectra, which will have a significant impact on the performance of photovoltaic panels.".
In this recent paper published in the journal Renewable Energy, titled "Characterization of Glass Surface Fouling and Its Impact on Optical and Solar Photovoltaic Performance," Markides and colleagues explained that the test samples were made from low iron glass specimens. In the solar energy industry, these test pieces are often used to encapsulate the top layer of photovoltaic modules. They collected glass samples at the end of each month in 2021, distinguishing between the rainy and dry seasons. In each collection period, researchers collected four samples with tilt angles of 0, 23, 45, and 90 degrees.
Subsequently, they sent these samples to London for transmittance testing. Analysis shows that the relative transmittance of horizontal samples decreases by 65% during the rainy season, 68% during the dry season, and 64% throughout the year.
The research team added, "In contrast, the relative transmittance of vertical specimens decreased by 34%, 19%, and 31%, respectively. The average relative transmittance of wet specimens, dry specimens, and one-year specimens with three different tilt angles decreased by 44%, 49%, and 42%, respectively."
Based on these results, researchers calculated the expected power loss of single crystal photovoltaic modules under standard test conditions (i.e. radiation intensity of 1000 watts/square meter and temperature of 25 degrees Celsius).
They added, "The relative transmittance decrease measured using samples from the rainy season, dry season, and annual levels corresponds to a relative decrease in predicted power generation of 67%, 70%, and 66%, respectively. Based on a local tilt angle of 23 degrees, the monthly relative transmittance loss is estimated to be about 30%, resulting in a decrease of about 30% in the equivalent relative photovoltaic power at the research site each month."
Then, scientists analyzed the characteristics of soil particles using X-ray and electron microscopy. Due to all glass samples being taken from the same location, scientists assume that their dirt has identical material characteristics. Therefore, they only analyzed horizontal glass specimens during the rainy and dry seasons, as well as throughout the year.
They emphasized, "The X-ray diffraction (XRD) results indicate that the annual level of sand and dust pollution test pieces contain various minerals, such as silicon dioxide, calcium carbonate, calcium magnesium carbonate, titanium dioxide, iron carbide, and aluminum silicate. The element distribution map focuses on the compounds reported by XRD analysis. The most important element is silicon (Si), while the remaining elements include carbon (C), oxygen (O), sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), aluminum (Al), calcium (Ca), and iron (Fe)."
Researchers also found that the amount of PM10 particles in dry season samples is higher than that in rainy season samples. PM10 is inhalable particulate matter with a diameter less than 10 microns. They explained in the paper, "Research has also shown that periodic rainfall can naturally clean up accumulated large particles, but cannot remove small particles."
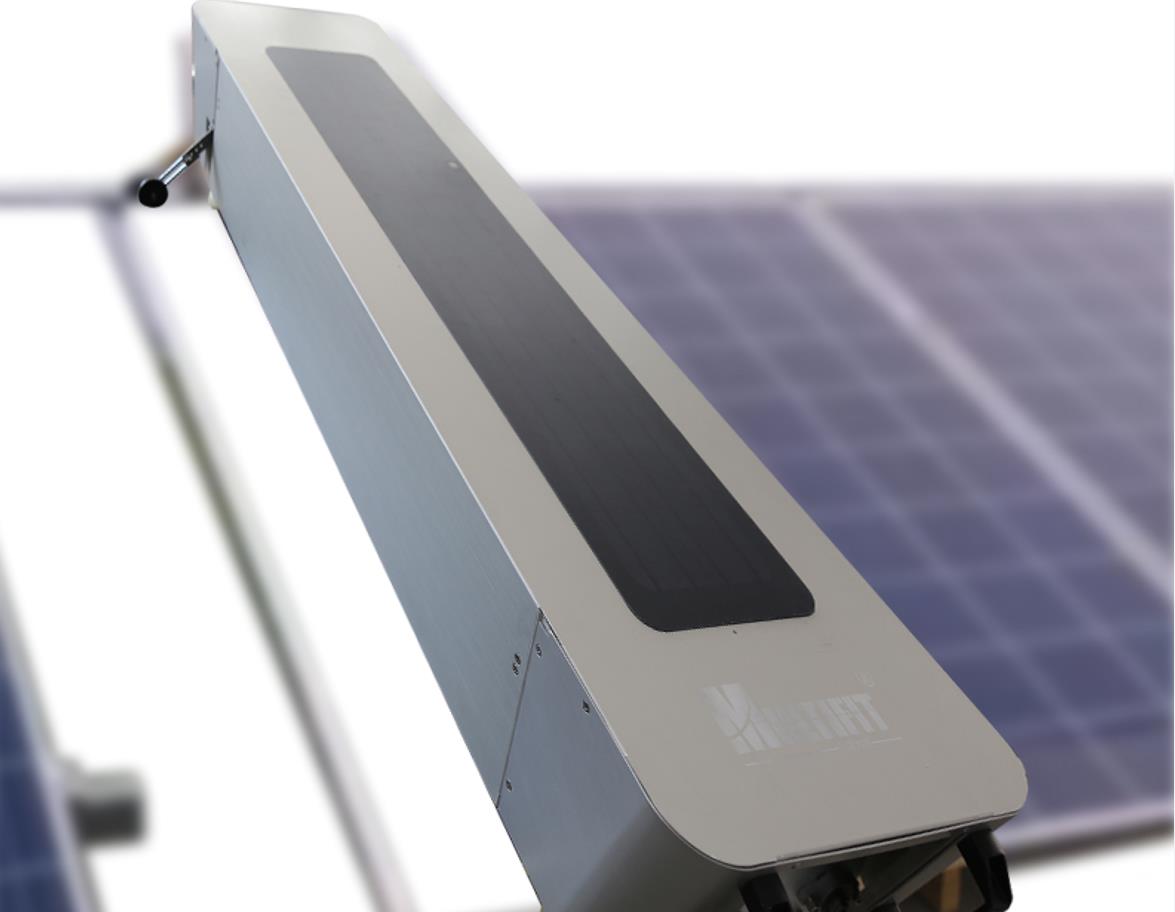
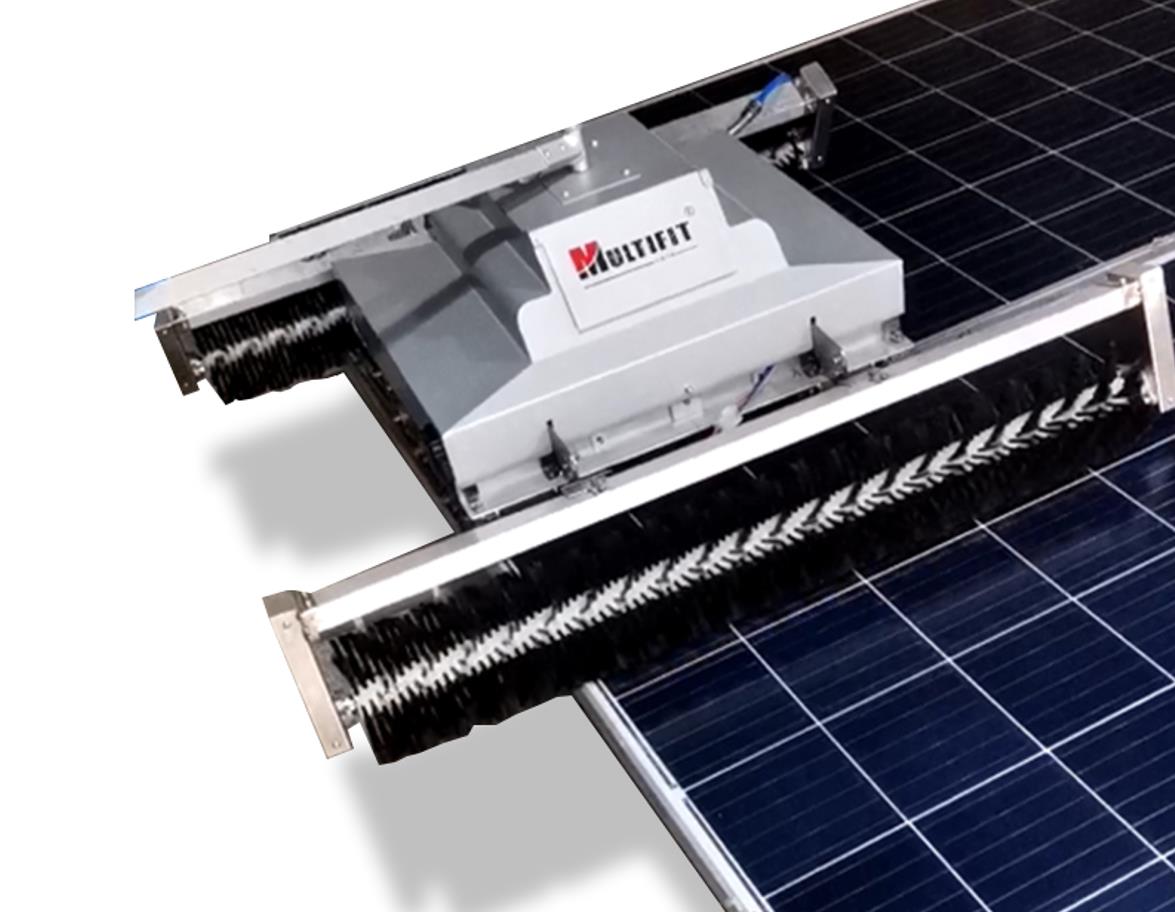
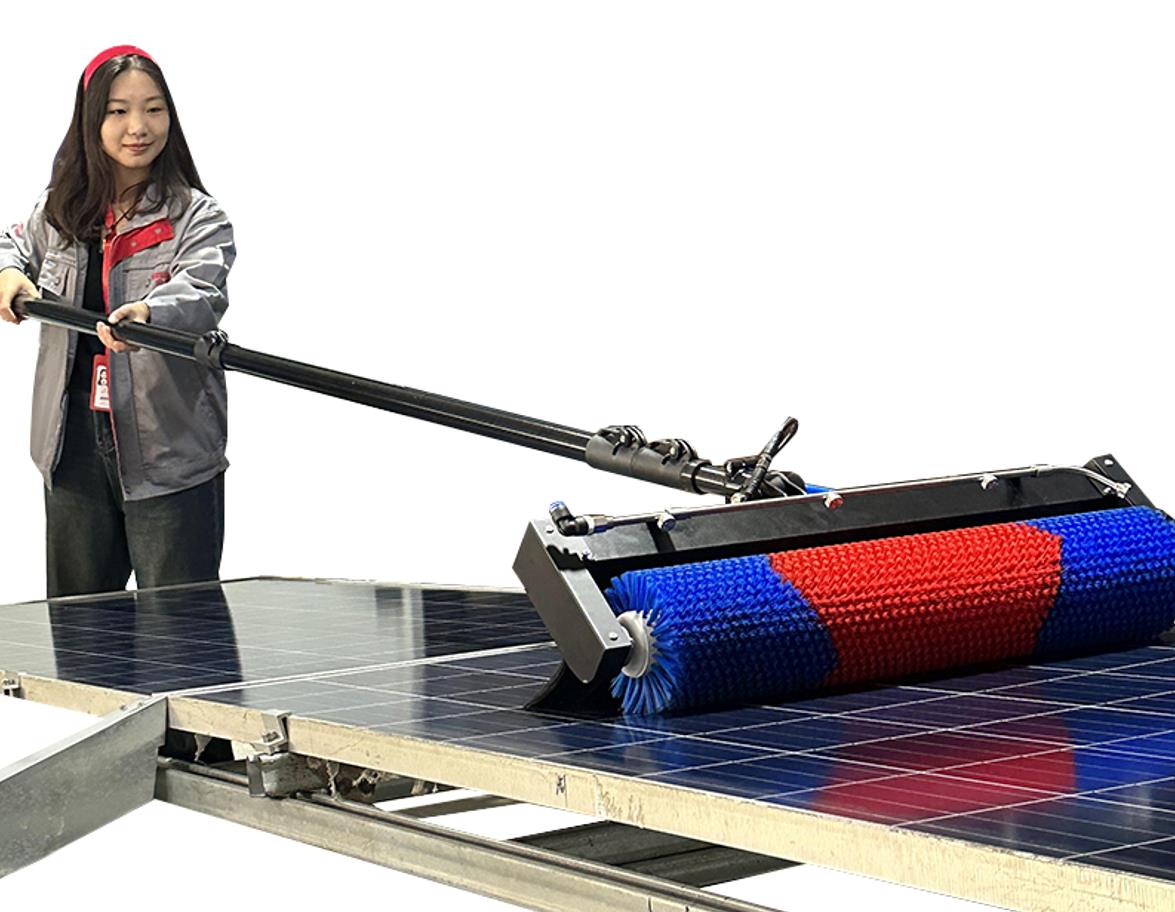
Therefore, relying solely on rainfall to achieve self-cleaning of solar panels is unreliable and requires the use of cleaning equipment for cleaning. Multifit Solar has been dedicated to researching photovoltaic cleaning for six years, and has developed various equipment such as handheld semi-automatic cleaning brushes and fully automatic cleaning machines to meet your cleaning needs in different scenarios.
Post time: Mar-26-2024